TSPSC Group 2 Syllabus comprises with 4 papers as mentioned below.
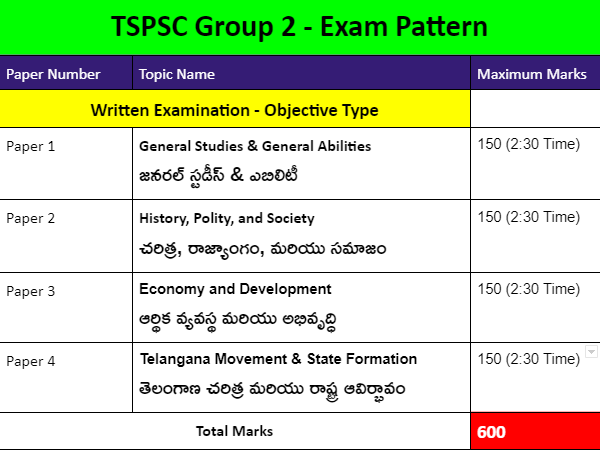
Paper 1 – General Studies and General Abilities
- Current Affairs – Regional, National & International.
- International Relations and Events.
- General Science; India’s Achievements in Science and Technology
- Environmental Issues; Disaster Management – Prevention and Mitigation Strategies.
- World Geography, Indian Geography and Geography of Telangana State.
- History and Cultural Heritage of India.
- Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
- Policies of Telangana State.
- Social Exclusion, Rights Issues and Inclusive Policies.
- Logical Reasoning; Analytical Ability and Data Interpretation.
- Basic English. ( 10th Class Standard)
Paper 2 – HISTORY, POLITY AND SOCIETY
I. Socio-Cultural History of India and Telangana.
- Salient features of Indus Valley Civilization: Society and Culture. -Early and Later, Vedic Culture; Religious Movements in Sixth Century B.C. – Jainism and Buddhism. Socio, Cultural and Economic Contribution during Mauryas, Guptas, Pallavas, Chalukyas and Cholas – Administrative System. Art and Architecture – Harsha and the Rajput Age.
- The Establishment of Delhi Sultanate-Socio-Economic, Cultural Conditions and Administrative System under the Sultanate –Sufi and Bhakti Movements. The Mughals: Socio-Economic and Cultural Conditions; Language, Literature, Art and Architecture. Rise of Marathas and their contribution to Culture; Socio-Economic, Cultural conditions in the Deccan under the Bahamani’s and Vijayanagara – Literature, Art and Architecture.
- Advent of Europeans: Rise and Expansion of British Rule: Socio-Economic and Cultural Policies – Cornwallis, Wellesley, William Bentinck, Dalhousie and others. The Rise of Socio-Religious Reform Movements in the Nineteenth Century. Social Protest Movements in India –Jotiba and Savithribai Phule, Ayyankali, Narayana Guru, Periyar Ramaswamy Naicker, Gandhi, Ambedkar etc. Indian Freedom Movement – 1885- 1947.
- Socio-Economic and Cultural conditions in Ancient Telangana- Satavahanas, Ikshvakus, Vishnukundins, Mudigonda and Vemulawada Chalukyas. Religion, Language, Literature, Art and Architecture; Medieval Telangana – Contribution of Kakatiyas, Rachakonda and Devarakonda Velamas, Qutub Shahis; Socio – Economic and Cultural developments: Emergence of Composite Culture. Fairs, Festivals, Moharram, Urs, Jataras etc.
- Foundation of AsafJahi Dynasty- from Nizam –ul- Mulk to Mir Osaman Ali Khan – SalarJung Reforms; Social and Economic conditions-Jagirdars, Zamindars, Deshmuks, and Doras- Vetti and Bhagela system and position of Women. Rise of Socio-Cultural Movements in Telangana: Arya Samaj, Andhra Maha Sabha, Andhra Mahila Sabha, Adi-Hindu Movements, Literary and Library Movements. Tribal and Peasant Revolts: Ramji Gond, Kumaram Bheemu, and Telangana Peasant Armed Struggle – Police Action and the End of Nizam Rule.
II. Overview of the Indian Constitution and Politics
- Evolution of the Indian Constitution – Nature and salient features – Preamble.
- Fundamental Rights – Directive Principles of the State Policy – Fundamental Duties.
- Distinctive Features of the Indian Federalism – Distribution of Legislative, Financial and Administrative Powers between the Union and States.
- Union and State Government – President – Prime Minister and Council of Ministers; Governor, Chief Minister and Council of Ministers – Powers and Functions.
- Indian Constitution; Amendment Procedures and Amendment Acts.
- Rural and Urban Governance with special reference to the 73rd and 74th Amendment Acts.
- Electoral Mechanism: Electoral Laws, Election Commission, Political Parties, Anti 33 defection Law and Electoral Reforms.
- Judicial System in India – Judicial Review; Judicial Activism; Supreme Court and High Courts.
- a) Special Constitutional Provisions for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes,
Backward Classes, Women, Minorities and Economically Weaker Sections (EWS).
b) National Commissions for the Enforcement – National Commission for Scheduled Castes,Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes, Women, Minorities and Human Rights. - National Integration issues and challenges: Insurgency; Internal Security; Inter-State Disputes.